Magnesium is an important mineral essential for maintaining overall health. It supports heart health, improves mood, and helps with sleep, among other vital functions in the body. This article examines the main roles of magnesium, its many health benefits, and the best dietary sources to ensure you get enough. It will also cover possible side effects and precautions, explaining why magnesium should be a key part of your wellness routine.
Key Takeaways:Magnesium plays a crucial role in our overall health, with benefits ranging from heart health and blood pressure management to improved mood and better sleep.Good sources of magnesium include foods like spinach and almonds, as well as supplements. Consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate dosage recommendations.While magnesium is generally safe for most people, it’s important to be aware of potential side effects and interactions with medications. Prioritizing magnesium intake can have a positive impact on our overall well-being.
What is Magnesium?
Magnesium is an important mineral involved in many body functions, like protein synthesis, muscle function, and neurotransmitter regulation. You can find it in foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Magnesium also helps with DNA and RNA synthesis, energy production, and maintaining normal heart rhythms. Not getting enough magnesium can cause health issues like fatigue, muscle cramps, and serious conditions such as osteoporosis and high blood pressure.
To maintain healthy magnesium levels, people should include magnesium-rich foods in their diets and consider supplements if advised by a doctor, especially if they have risk factors.
Ensuring enough magnesium intake supports overall health and may help prevent disorders related to magnesium deficiency.
Functions of Magnesium in the Body
Magnesium is important for many functions in the body, such as muscle function, heart rhythm, and neurotransmitter activity.
It is essential for protein synthesis, aiding in muscle repair and growth, which is crucial for athletes and active individuals. For more information on the importance of magnesium, check out this article on the health benefits of magnesium.
Additionally, magnesium helps maintain energy levels, supports calcium regulation for bone health, and aids in the proper function of insulin, a hormone vital for blood sugar control.
Key Roles and Importance
Magnesium is important for various body functions, significantly supporting heart health, mental wellness, and inflammation control. This essential mineral helps maintain a healthy heart rhythm and is linked to managing anxiety and sleep issues. It enhances the body’s ability to absorb and use vitamins and minerals effectively.
Magnesium presence is linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases as it helps regulate blood pressure and supports endothelial function. It also eases muscle tension and promotes relaxation, which can reduce anxiety levels, benefiting those dealing with stress.
Its anti-inflammatory properties strengthen the immune system and fight chronic inflammation, which is involved in many health issues.
Incorporating magnesium into your wellness routine can improve heart health and overall well-being.
Health Benefits of Magnesium
Magnesium offers numerous health benefits, affecting both physical and mental well-being. This important mineral can help reduce inflammation in the body, which may lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and diabetes.
Additionally, magnesium supports mental health by reducing anxiety and improving sleep quality, making it beneficial for those experiencing stress or sleep problems.
Key Data on Magnesium Health Benefits
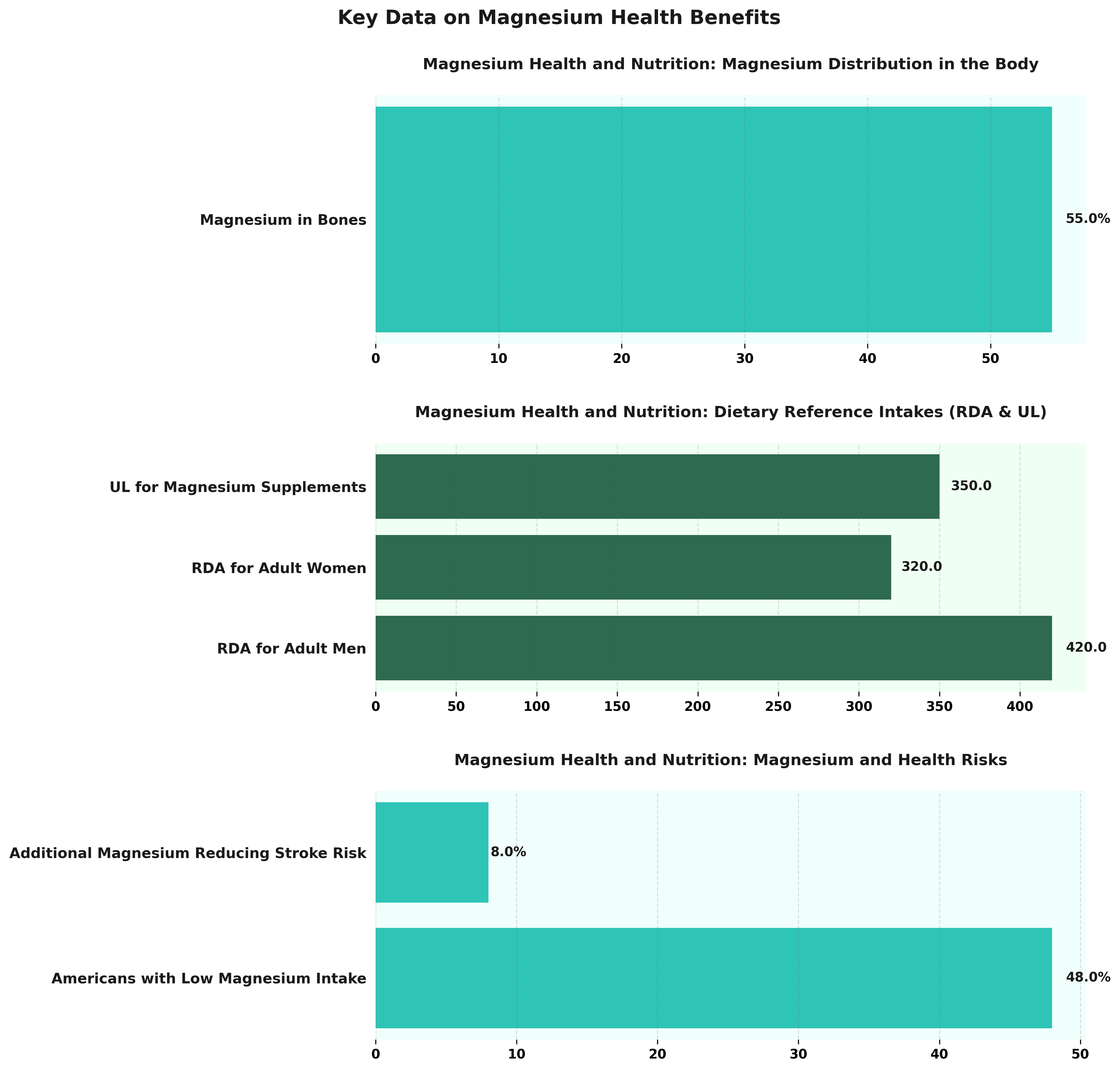
The Key Data on Magnesium Health Benefits provides insights into the role of magnesium in the body, dietary recommendations, and its impact on health risks. This information is crucial for understanding how magnesium contributes to overall health and the importance of maintaining adequate intake levels.
Magnesium Health and Nutrition highlights the significant presence of magnesium in the body, with 55% stored in bones. This emphasizes magnesium’s role in bone structure and health, indicating the necessity of this mineral for maintaining bone strength and density.
- Dietary Reference Intakes (RDA & UL): The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for adult men is 420 mg, and for adult women, it is 320 mg. These values reflect the amount needed to support body functions and prevent deficiencies. However, the Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for magnesium supplements is set at 350 mg to prevent adverse effects from excessive intake, highlighting the need for balanced consumption through diet and supplements.
The data also reveals health risks associated with inadequate magnesium levels. 48% of Americans have a low magnesium intake, indicating a widespread deficiency that could lead to health issues like muscle cramps, mental health disorders, and cardiovascular problems. Furthermore, increasing magnesium intake has been associated with an 8% reduction in stroke risk, underscoring its protective effects on cardiovascular health.
Overall, these statistics stress the importance of sufficient magnesium intake for bone health, preventing deficiencies, and reducing health risks. Individuals and healthcare providers should ensure dietary sources rich in magnesium, such as leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains, are included in daily nutrition to maintain optimal health.
Improving Heart Health
Magnesium is important for heart health because it helps control blood pressure and maintain a steady heart rhythm, which are key for lowering heart disease risk. Adequate magnesium levels help relax blood vessels, improving cardiovascular function and potentially preventing problems like high blood pressure.
Studies indicate that people with higher magnesium intake have a lower risk of heart-related diseases. For example, a meta-analysis in ‘Circulation’ found that each 100 mg increase in daily magnesium intake was linked to a 22% lower risk of developing high blood pressure.
Magnesium is crucial for the heart’s electrical functions, helping regulate heartbeats and preventing arrhythmias. It promotes a healthy vascular tone and reduces arterial stiffness, supporting optimal blood pressure and stable heart rhythms.
Therefore, maintaining proper magnesium levels is essential for those aiming to improve heart health.
Managing Blood Pressure
Magnesium helps manage blood pressure and improves insulin sensitivity. Getting enough magnesium can reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including heart conditions, by promoting healthy blood flow and vascular function.
About 60% of adults in the U.S. do not consume enough magnesium daily, which can lead to high blood pressure and a greater risk of hypertension. A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that higher magnesium intake is linked to lower blood pressure, especially in people with hypertension.
Magnesium regulates blood vessel function and affects the renin-angiotensin system, playing a key role in heart health. Eating foods rich in magnesium may help maintain normal blood pressure and reduce the risk of other chronic diseases, improving overall well-being.
Reducing Inflammation
Reducing inflammation is a key benefit of magnesium, especially in lowering levels of C-reactive protein, which indicates inflammation. By supporting the body’s natural anti-inflammatory processes, magnesium may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases related to inflammation.
Research shows that adequate magnesium intake is linked to lower systemic inflammation, important because chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and arthritis often result from prolonged inflammation.
A study in the Journal of the American Heart Association found that people with higher magnesium levels had lower C-reactive protein levels, suggesting protection against such diseases. Another study in the European Journal of Nutrition showed that increasing magnesium intake through diet significantly reduces inflammatory markers, highlighting its essential role in health and well-being.
Boosting Mood and Mental Health
Magnesium is important for improving mood and mental health because it helps regulate neurotransmitters needed for emotional well-being. Studies show that adequate magnesium levels can reduce anxiety and improve mood stability, making it essential for mental health.
Research indicates that a lack of magnesium may be linked to higher levels of anxiety and depression, highlighting the mineral’s role in brain function. For example, a 2017 study in the journal Nutrients found that people with lower magnesium intake had more mood swings and anxiety.
Magnesium helps produce serotonin, known as the ‘feel-good chemical,’ which supports a balanced mood. Therefore, including magnesium-rich foods like spinach, nuts, and whole grains in your diet may help improve emotional health naturally.
Promoting Better Sleep
Magnesium helps improve sleep by regulating neurotransmitters that affect sleep patterns. Having enough magnesium can lessen sleep problems and anxiety, leading to deeper and more restorative sleep.
Research indicates that magnesium is important in producing melatonin, the hormone that controls the sleep-wake cycle. It also affects gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that encourages relaxation and reduces nervous system activity. Magnesium benefits include improvement in sleep issues by promoting better rest and relaxation.
A study in the Journal of Research in Medical Sciences found that participants who took magnesium supplements reported better sleep quality and longer sleep duration. By promoting balanced brain chemistry and neurotransmitters, magnesium not only helps with falling asleep but also enhances magnesium for anxiety reduction and improves the overall depth of sleep experienced throughout the night.
Supporting Bone Health
Supporting bone health is a key function of magnesium, as it plays a vital role in calcium regulation, which is essential for maintaining bone density and preventing conditions like osteoporosis. Adequate magnesium intake is important for optimal bone health throughout life, including preventing chronic diseases like osteoporosis.
Research shows that magnesium deficiency can impair calcium metabolism, affecting bone formation and breakdown. Studies published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research have shown a clear link between higher dietary magnesium intake and improved bone mineral density, emphasizing the importance of nutrient absorption for bone health.
A meta-analysis of various clinical trials found that individuals with optimal magnesium levels were less likely to develop osteoporosis, highlighting its protective effects.
Including magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, and whole grains in your diet can significantly strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures as you age.
Sources of Magnesium
Magnesium can be obtained from various sources, including foods and supplements. Leafy green vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains are excellent natural sources of magnesium, essential for maintaining magnesium requirements and recommended intake.
For those who have difficulty meeting their magnesium needs through diet alone, supplements can be a helpful option.
Foods High in Magnesium
Foods rich in magnesium include leafy greens, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains. Adding these to your diet helps maintain good health and reduces the risk of magnesium deficiency.
- Spinach and kale are great sources, providing magnesium along with vitamins A, C, and K, which are important for body functions and immune health.
- Almonds and cashews are high in magnesium and also offer healthy fats and protein, making them a good snack for energy.
- Pumpkin and chia seeds can be added to smoothies or salads to boost magnesium intake and also provide fiber and antioxidants.
- Black beans and lentils supply a lot of magnesium and plant-based protein, benefiting heart health and digestion.
- Whole grains like brown rice and quinoa increase magnesium levels and offer essential nutrients that support overall well-being.
Supplements and Dosage Recommendations
Magnesium supplements can help individuals increase their magnesium intake, with magnesium citrate being a popular choice due to its high absorption rate. It’s important to adhere to recommended guidelines to avoid magnesium toxicity and magnesium overdose from taking too much.
There are different forms of magnesium supplements, such as: What Are the Health Benefits of Magnesium?
- 1: Magnesium oxide
- 2: Magnesium glycinate
- 3: Magnesium malate
Each with varying absorption rates and benefits. For example, magnesium glycinate is often chosen for its high absorption and calming effects, making it a good option for those looking to improve relaxation and sleep quality.
Typical recommended dosages range from 200 to 400 mg per day, based on individual health needs and dietary intake. Exceeding these amounts can cause side effects like diarrhea and abdominal discomfort, so it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions
Magnesium is important for health, but be aware of potential side effects, such as magnesium toxicity, magnesium overdose, and magnesium interactions with certain medications.
Large doses, especially from supplements, can cause negative effects. Its interaction with some medications or substances like caffeine may also affect how it works and its safety.
Possible Risks and Interactions
Risks and interactions with magnesium largely involve its interactions with various medications and dietary substances. For example, proton pump inhibitors like Dexilant and Nexium can affect magnesium absorption, while caffeine effects may reduce its effectiveness, especially in people with chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
Those taking diuretics or certain heart medications need to be cautious, as these can decrease magnesium levels or alter absorption rates, affecting insulin sensitivity and nutrient absorption.
Individuals with conditions like diabetes or kidney disorders should regularly monitor their magnesium levels since imbalances can worsen health issues.
Dietary habits also matter; high consumption of processed foods or excessive caffeine can complicate magnesium levels. This highlights the need for a balanced diet and possibly tailored supplementation based on individual health needs.
The Importance of Magnesium for Overall Health and Well-being
Magnesium is vital for health as it supports many bodily functions and prevents deficiency. This mineral is associated with lowering the risk of chronic diseases such as types of diabetes and heart disease, and improving mental and physical health, making it essential for everyone.
Adequate magnesium intake supports processes such as energy production, protein synthesis, and maintaining healthy bones and muscles. Research shows magnesium’s role in regulating blood pressure and glucose levels, which helps prevent heart disease and diabetes.
It also supports a healthy nervous system, helping with mood regulation and reducing anxiety and depression risk. Ensuring enough magnesium in your diet, through food or supplements if needed, can significantly improve health and prevent deficiencies that may cause long-term problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Health Benefits of Magnesium?
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Here are some of the most notable health benefits of magnesium:
How does magnesium benefit the body?
Magnesium is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including energy production, nerve function, muscle contraction, and protein synthesis. It also plays a role in maintaining healthy bones, heart function, and muscle function.
Can magnesium help with muscle cramps?
Yes, magnesium is known to help relax muscles and reduce muscle cramps. It works by regulating calcium levels and calcium regulation, which can contribute to muscle cramps when imbalanced.
In what ways does magnesium support heart health?
Magnesium has been shown to help prevent and manage high blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease and prehypertension. It also supports proper heart rhythm and reduces inflammation and chronic inflammation in the body, contributing to its anti-inflammatory effects.
What are the benefits of magnesium for mental health?
Studies have shown that magnesium may help improve mood, reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, and enhance cognitive function. It may also be beneficial in treating migraines and insomnia, showcasing its magnesium roles in mental health.
Can magnesium help with PMS symptoms?
Yes, magnesium has been found to relieve symptoms associated with premenstrual syndrome (PMS), such as bloating, cramps, and mood swings. It may also be helpful in reducing menstrual migraines, highlighting its importance in women’s health and magnesium for PMS.
How can I incorporate more magnesium into my diet?
Magnesium can be found in many foods, including leafy greens, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes, which are excellent magnesium-rich foods. You can also take magnesium supplements if you are not getting enough through your diet, which are critical magnesium sources to meet daily dietary allowance.
Ancient herbs.
Sourced from where they grow wild.
Henna, Bhringraj, Neem, Shikakai — single-ingredient powders grown in their native Indian regions, stone-ground and sealed within 72 hours of harvest. No fillers, no synthetic additives. Just the plant.
7 ISO certifications · Free shipping on orders ₹599+ · Ships from Noida, India
🔬 Reviewed for Scientific Accuracy by:
With over 15 years of academic and clinical experience, Dr. Gautam oversees the scientific and editorial integrity of educational content related to herbs, nutrition, and wellness.
ResearchGate Profile | ORCID
All FarmPURE Blog content is reviewed by domain experts to ensure it reflects the highest standards of botanical integrity, scientific relevance, and practical guidance. Our mission is to promote better health and beauty through the power of organic herbs, spices, and plant-based wellness solutions.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog is intended for general wellness and educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Dr. Rashmi Gautam as scientific reviewers only, and do not provide or endorse personalized medical recommendations. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before making decisions related to your health.

