Millet is an ancient cereal grain that has been a staple food in southern Asia and Africa for thousands of years. It is commonly found in countries including India, Pakistan, China, and Egypt. It is also grown in the United States and other western countries today. Millet is a small-grained cereal plant with small grains with a husk covering. The grain itself looks like a small brick or teacup. Millet is rich in protein, dietary fiber, and several vitamins and minerals such as iron, thiamin, riboflavin, and niacin.
These nutrients are beneficial to people of all ages. You may not be familiar with it yet, but millet will soon become a staple food for many households as more people choose to include it in their diets for its nutritional benefits as well as its affordability. In this article, we’ll talk about what is millet and what is it used for in your daily meals to get more nutrients while spending less money at the same time.
What is millet, and where does it come from?
Millet is an ancient cereal grain that has been a staple food in southern Asia and Africa for thousands of years. It is commonly found in countries including India, Pakistan, China, and Egypt. It is also grown in the United States and other western countries today. Millet comes from the Latin word millere, which means “thousand”. For this reason, it was believed to have originated from the thousand grains of barley used by a farmer called Milletarius, who lived during the time of Christ. The grains are usually about 1/4 inch (6 mm) long. They come in two colour varieties: white and red. The red variety is more common outside of North America and Europe.

The nutritional benefits of millet
Millet is a whole grain, and a variety of healthy foods can be prepared from it, including breads, pasta, and porridge. It has high levels of dietary fiber and a low glycemic index. This means that it takes longer for the body to break down its carbohydrates into sugar, which helps lower blood sugar levels in people with diabetes.
Millet also has beneficial amounts of magnesium, iron, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, phosphorous, zinc, copper and manganese. Many people have found that millet also benefits heart health through the vitamin B1 it contains, which contributes to heart health by lowering cholesterol levels and decreasing general inflammation in the body. Millet can also be used in soups, salads, and many different types of breads because it’s not only low-glycemic but also gluten-free!
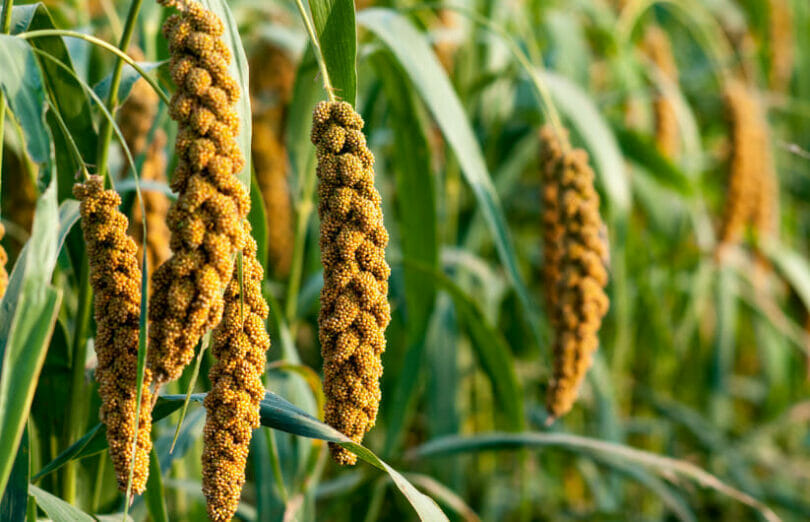
What does millet look like and taste like?
Millet is a small-grained cereal plant that has been around for thousands of years and is commonly found in countries including India, Pakistan, China, and Egypt. The grain itself looks like a small brick or teacup. Millet is rich in protein, dietary fiber, and several vitamins and minerals such as iron, thiamin, riboflavin, and niacin.
These nutrients are beneficial to people of all ages. What does millet taste like? Some people think it tastes like oatmeal or cornmeal; others say it tastes similar to quinoa or rice. Regardless of what you think it tastes like, you’ll be surprised at how easy and quick it is to make millet into meals you can feel good about eating daily!
Health benefits of millet for food
Millet is a cereal grain that has been eaten for over 10,000 years. It is loaded with nutrients and has low calories. It is not overly processed, making it a healthy option for those on a budget who want to incorporate grain into their diet without worrying about its healthfulness.
Additionally, millet can be ground into flour and used to make gluten-free bread and cereals. Other millet recipes include pancakes, waffles, biscuits, cookies, muffins, granola bars, and many other treats that are easy to make at home. As an ancient food staple in Africa and Asia for thousands of years, millet is one of the most nutritious grains you can find. Millet provides more fiber than wheat or rice, meaning you’ll feel full faster after eating it. Additionally, if you’re looking for a gluten-free option and a low-calorie food source, try adding millet to your diet today!

How to use millet in your daily meals?
The most common way to use millet is cereal. You can prepare it the same way you would prepare oatmeal, rice, or wheat cereals. For example, you can prepare some millet and put it on the stove with water and spices for a quick and easy breakfast. To use millet as a pasta replacement, cook it in boiling water with salt and seasonings like garlic powder or butter.
You may also want to try using it as a substitute for regular flour in bread or muffins. You could also make your millet porridge by cooking it with milk or hot cereal mixture (like oatmeal) before serving. If you are looking for extra flavour, you may want to add sugar, honey, cinnamon, vanilla extract, nutmeg, cardamom pods, ginger root, nutmeg powder or other spices to your millet porridge before serving.
Some benefits of consuming millet with B Vitamin Complex (BVMC)
Millet has a high concentration of B vitamins, which are important nutrients for healthy digestion and metabolism. B vitamins help the body break down carbohydrates and fat in food, support immune function like vitamin C, and improve mood as they decrease stress. Millet is also a good source of fiber which reduces cholesterol levels and regulates blood sugar levels.
Consumption of millet with BVMC can help many people trying to lose weight, eat healthier, or reverse metabolic syndrome. It is an affordable option with nutritional benefits for those with food allergies or sensitivities, such as gluten-free or vegan diets. With these benefits in mind, it is no wonder that more consumers are turning to this plant grain to increase their nutrient intake while spending less on groceries.
Conclusion
Millet is a grain that is part of the grass family. Millet is the most commonly used grain in Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and the Middle East. It is a good protein, vitamin and mineral source and is gluten-free. It is a good alternative to rice and wheat for a healthy grain to add to your diet.

FAQs
What are the benefits of millet?
The benefits of millet include being a great source of protein, dietary fiber, iron, thiamin, niacin and zinc. It is also high in calcium and potassium. It helps in weight loss by cutting down extra fat from your body. It also lowers bad cholesterol and blood pressure. Millet also helps keep your bones strong and healthy by providing calcium and iron. It also aids in the production of red blood cells. All these benefits result in a healthier lifestyle.
What are the benefits of including millet in your diet?
There are many benefits to including millet in your diet. One of the most important benefits is that it is low in fat and saturated fat. It also contains dietary fiber, protein, and many other nutrients that play a role in your health. Another benefit of millet is that it may help lower cholesterol levels and triglycerides. It may also improve glucose tolerance and help lower blood pressure. Millet is also a good source of calcium and vitamin B-6, both important for bone health and proper nervous system function. Additionally, millet may reduce the risk of heart disease due to its high content of beta-carotene and lutein/zeaxanthin, two antioxidants that may reduce the risk of heart disease.
What are the health benefits of millet?
Protein: Millet is a good source of protein. It contains all the essential amino acids in the right proportions. It is especially rich in lysine, an important amino acid for children and pregnant women. Protein contributes greatly to maintaining bone mass, which is important for building and maintaining muscles and tissues. Additionally, protein helps the body absorb vital nutrients and keep your blood pressure normal.
Vitamin A: Millet also contains a good amount of vitamin A. This vitamin plays an important role in your eyesight and immune system. Vitamin A is also essential for healthy skin, breast tissue, and reproductive systems.
Vitamin B: Vitamin B is found in high concentrations in millet. This vitamin helps your body utilize carbohydrates and protein. It also contributes to normal growth and development. Vitamin B improves lung function in children and supports nerve function.
Vitamin C: This water-soluble vitamin is a powerful antioxidant and helps maintain healthy skin and gut function. It also contributes to normal growth and development and protects your heart from oxidative damage. Folate is an important nutrient that helps prevent congenital disabilities by helping your body cells reproduce properly. Folate plays a vital role in DNA synthesis, red blood cell production, protein synthesis, and many other cellular processes.
Ancient herbs.
Sourced from where they grow wild.
Henna, Bhringraj, Neem, Shikakai — single-ingredient powders grown in their native Indian regions, stone-ground and sealed within 72 hours of harvest. No fillers, no synthetic additives. Just the plant.
7 ISO certifications · Free shipping on orders ₹599+ · Ships from Noida, India
🔬 Reviewed for Scientific Accuracy by:
With over 15 years of academic and clinical experience, Dr. Gautam oversees the scientific and editorial integrity of educational content related to herbs, nutrition, and wellness.
ResearchGate Profile | ORCID
All FarmPURE Blog content is reviewed by domain experts to ensure it reflects the highest standards of botanical integrity, scientific relevance, and practical guidance. Our mission is to promote better health and beauty through the power of organic herbs, spices, and plant-based wellness solutions.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog is intended for general wellness and educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Dr. Rashmi Gautam as scientific reviewers only, and do not provide or endorse personalized medical recommendations. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before making decisions related to your health.